Ares Market Official Information 2026
Comprehensive security guide and marketplace information for The platform. Learn about anonymous marketplace operations, privacy tools, and cryptocurrency security. This official educational resource provides verified information about Ares marketplace security and darknet trading.
Current Cryptocurrency Prices
Real-time cryptocurrency market data relevant for anonymous transactions in darknet marketplaces. Ares market primarily accepted Monero (XMR) for enhanced privacy, with Bitcoin (BTC) as secondary option. Prices updated every 60 seconds from CoinGecko API.
Data Source: Real-time prices from CoinGecko. Market prices may vary across exchanges. Always verify current rates before transactions on any marketplace.
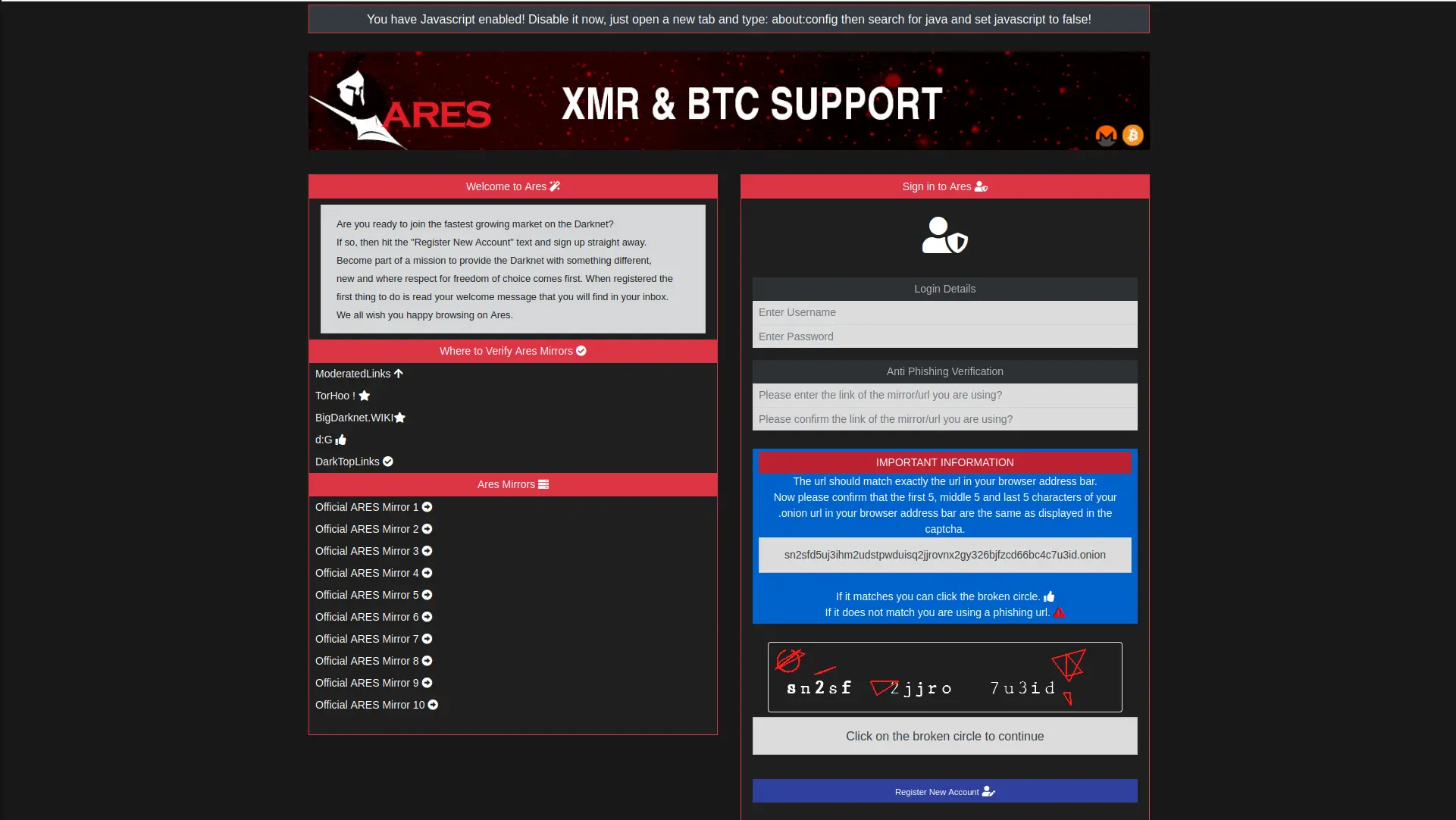
Cryptocurrency payment security in anonymous marketplaces
What Was Ares Market?
Ares market was a darknet marketplace launched in 2021 that operated as a wallet-less platform for anonymous transactions. The The platform claimed to offer enhanced security features including mandatory PGP encryption, two-factor authentication, and a unique direct-pay system. At its peak in August 2024, Ares market hosted approximately 7,500 listings, 160 vendors, and 14,000 users according to professional cybersecurity analysis by DarkOwl.
The the platform positioned itself as a privacy-focused alternative to larger marketplaces, emphasizing Monero cryptocurrency for untraceable transactions. The The platform technical architecture claimed "wallet-less" operation where users deposited exact order amounts rather than maintaining marketplace balances, theoretically reducing centralized fund accumulation and exit scam risk.
Ares Market Key Features (When Operational)
- Wallet-less Direct-Pay System: Ares market generated per-order escrow addresses using HD wallets for Bitcoin and subaddresses for Monero. Users sent exact order amounts directly to unique addresses rather than depositing funds into marketplace wallets.
- Monero Primary Cryptocurrency: The official The platform prioritized Monero (XMR) for enhanced transaction privacy through ring signatures, stealth addresses, and RingCT protocol. Bitcoin was accepted as secondary option.
- Security Features: Ares market implemented mandatory PGP encryption for all communications, two-factor authentication using PGP keys, login phrase verification to prevent phishing, and QR code payment scanning for error reduction.
- Modern User Interface: The The platform featured clean, intuitive design with 57 subcategories alphabetically organized, grid layout for efficient browsing, and responsive interface praised as "excellent UX/UI design" in user reports.
- Competitive Commission: Ares market charged 4% vendor fees versus 5% industry standard, with variable vendor bonds ranging from 0.5-5 XMR based on listing limits and reputation requirements.
Why Ares Market Exit Scammed
Despite technical innovations and security marketing, The platform suffered from fundamental centralized architecture vulnerabilities. The official administrators controlled all escrow private keys, enabling unilateral access to funds despite "wallet-less" marketing claims. When trust collapsed in late 2024, Ares market executed a classic slow-exit scam pattern: gradual support degradation, selective withdrawal delays, ticket deletion, and eventual fund theft.
Historical precedents demonstrate centralized marketplaces inevitably exit scam or face law enforcement seizure. Similar markets including Nexus (January 2025, $15M stolen), Abacus (June 2025, $100M+ stolen after 4 years trusted operation), and Archetyp (June 2024, seized by Europol) followed identical trajectories. Ares market lasted approximately 2-4 years before exit scamming, consistent with median darknet marketplace lifespan.
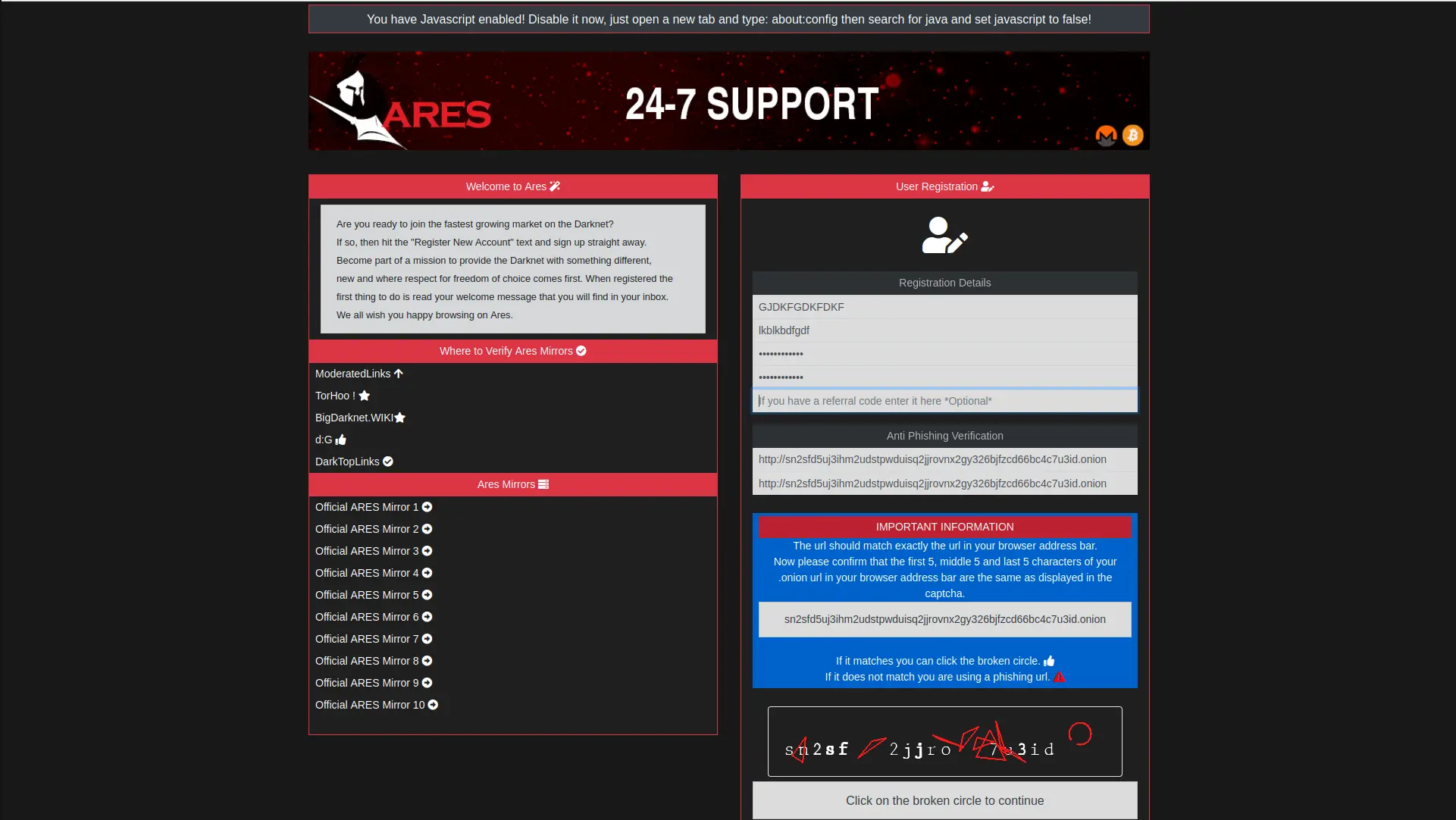
Example of modern darknet marketplace interface architecture
Understanding Exit Scam Patterns in Darknet Marketplaces
Exit scams represent the primary failure mode for centralized darknet marketplaces, occurring when administrators abruptly cease operations while stealing all escrowed user funds. Research analyzing marketplace lifespan data from 2011-2025 reveals that approximately 60-70% of all darknet platforms ultimately exit scam, with median operational duration of 8-14 months before theft execution. Understanding exit scam warning patterns helps users identify high-risk platforms before fund loss occurs.
Classic Exit Scam Progression
Typical exit scams follow predictable multi-stage pattern observable across dozens of historical marketplace failures. Initial phase features normal operation with responsive support, timely withdrawals, and active vendor community. Warning phase begins with selective scamming targeting large accounts first, withdrawal delays extending from hours to days then weeks, support ticket response times degrading from immediate to sporadic, and vendor complaints about unpaid finalized orders appearing on external forums like Dread.
Final phase demonstrates complete platform abandonment: support system goes dark with tickets deleted unread, withdrawal processing ceases entirely with funds trapped in escrow, administrators become unresponsive across all communication channels, directory listings disappear as moderators remove scam platforms, and user exodus accelerates as community warnings spread. Recent exit scams including Nexus (January 2025, $15M stolen after 14 months), Abacus (June 2025, $100M+ after 4 years trusted operation), and Wall Street Market (April 2019, $30M stolen) all exhibited these identical behavioral indicators.
Centralization Risk Fundamentals
Exit scams stem from fundamental centralized architecture where single administrator team controls all critical infrastructure: server access, database management, escrow cryptocurrency private keys, user authentication systems, and dispute resolution processes. This centralization creates structural incentive for theft - administrators accumulate millions in escrowed cryptocurrency accessible through unilateral action without user consent or technical barriers.
Technical "security features" marketed by platforms prove irrelevant against operator malice. Wallet-less systems reduce temptation by limiting fund accumulation but cannot prevent theft if administrators control escrow keys. PGP encryption protects against external eavesdropping but not administrator database access. Two-factor authentication prevents account hijacking but not platform-wide exit scam. Only true cryptographic decentralization through multisignature escrow or blockchain smart contracts eliminates exit scam capability - yet 95%+ of darknet marketplaces retain centralized control despite decentralization marketing claims.
Tor Network & Anonymous Browsing Security
The Tor network provides anonymous internet access essential for darknet marketplace browsing. Ares market, like all darknet markets, operated exclusively through Tor hidden services (.onion addresses) to protect user anonymity and evade law enforcement detection. Understanding Tor security is critical for anyone researching darknet marketplaces or darknet security practices.
Tor Browser Security Configuration
Accessing any marketplace including the former the platform requires proper Tor Browser configuration. Download Tor Browser exclusively from Tor Project official website to avoid malware-infected versions. Configure security level to "Safest" to disable JavaScript and plugins that could compromise anonymity through browser fingerprinting.
Critical Tor OPSEC principles for marketplace access: Never maximize Tor Browser window (creates unique screen resolution fingerprint), use Tails OS or Whonix for amnesia/isolation, never log into clearnet accounts through Tor, avoid downloading files that could execute outside Tor, and verify .onion addresses through multiple independent sources to prevent phishing.
Tor Network Limitations
Tor provides strong anonymity against network surveillance but cannot protect against marketplace operator malice. Ares market exit scam demonstrates that Tor anonymity is irrelevant when administrators control funds and user data centrally. Exit scams, selective scamming, and data breaches remain primary risks regardless of Tor protection.
Law enforcement has successfully de-anonymized Tor users through traffic correlation attacks, malware deployment, operational security mistakes, and marketplace server seizures. The Archetyp marketplace seizure (June 2024) and administrator arrest in Barcelona demonstrates Tor alone does not guarantee protection from law enforcement with sufficient resources and international cooperation.
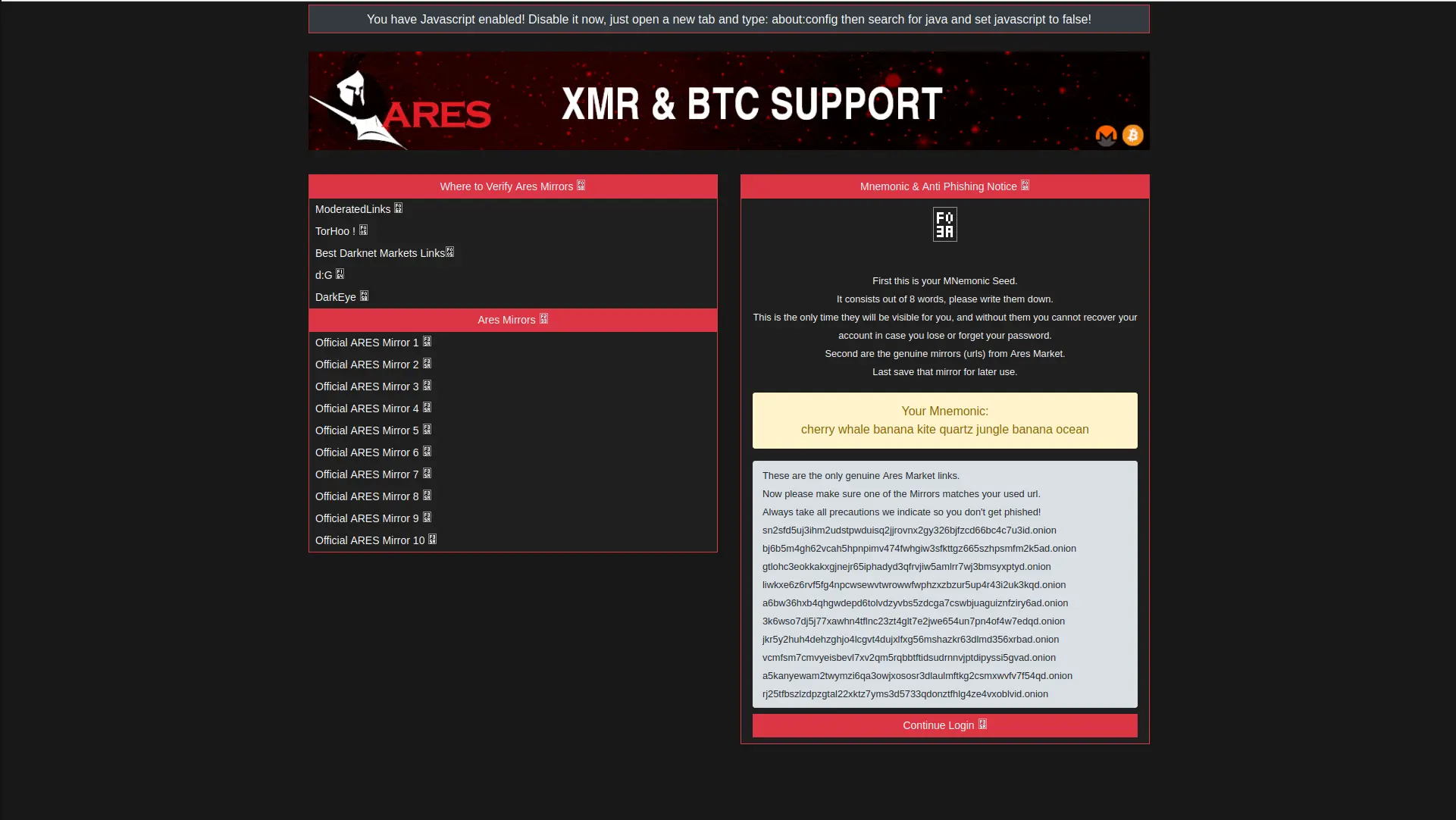
Tor network security architecture for anonymous marketplace access
Latest Privacy & Security News
Curated news about digital privacy, security developments, and cryptocurrency updates from trusted sources. News updated hourly from independent privacy advocates including the Electronic Frontier Foundation. Stay informed about privacy threats, encryption policy, and security research relevant to anonymous browsing and cryptocurrency use.
News Sources: EFF Deeplinks, and other privacy-focused publications.
PGP Encryption for Secure Communications
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) encryption is mandatory for darknet marketplace communications. Ares market required PGP for all vendor-buyer messages, address submissions, and dispute communications to prevent marketplace operators from accessing sensitive information. Even after The platform exit scam, understanding PGP remains essential for privacy protection.
PGP Implementation Guide
Generate PGP key pairs using GnuPG (GPG) open-source software, available for Windows (GPG4Win), macOS (GPG Suite), and Linux (native). Create 4096-bit RSA keys for maximum security, set strong passphrase using KeePassXC password manager, and backup private key securely to encrypted storage using VeraCrypt.
The the platform used PGP signatures to verify administrator communications and prevent phishing. Users could verify official The platform announcements by checking PGP signature against published public key. Exit scam warning signs included unsigned messages, support refusing PGP communication, or signature verification failures indicating phishing attempts or compromised accounts.
PGP Best Practices
Never upload private PGP key to any marketplace or website, encrypt all addresses and sensitive data before marketplace submission, verify vendor PGP keys through multiple sources, use separate keys for different marketplaces to prevent cross-identification, and regularly rotate keys (annually minimum) to limit damage from potential key compromise.
When Ares market exit scammed, users who encrypted addresses with vendor PGP keys (not marketplace PGP) had better protection against exposure. However, marketplace database seizures still expose order metadata (amounts, timestamps, cryptocurrency addresses) even when message content remains encrypted.
Cryptocurrency Privacy & Transaction Security
Cryptocurrency privacy is critical for darknet marketplace transactions. Ares market primarily accepted Monero specifically for enhanced privacy compared to Bitcoin's transparent blockchain. Understanding cryptocurrency tracing risks and privacy technologies remains essential knowledge even after marketplace exit scams.
Monero Privacy Technology
Monero provides privacy through three cryptographic technologies: ring signatures that hide transaction sender among decoy outputs, stealth addresses that obscure recipient address on blockchain, and RingCT (Ring Confidential Transactions) that hide transaction amounts. Download Monero official wallet from GetMonero.org and run full node for maximum privacy.
The platform accepted Monero for all transactions, eliminating Bitcoin tracing risks from blockchain analysis firms like Chainalysis and CipherTrace. However, Monero privacy doesn't protect against marketplace exit scams - Ares market administrators still stole funds regardless of Monero's transaction privacy.
Bitcoin Privacy Risks
Bitcoin transactions are permanently recorded on transparent public blockchain, enabling law enforcement tracing through controlled deliveries, exchange KYC (Know Your Customer) data, clustering analysis, and chain analysis software. Even years after transactions, Bitcoin addresses can be de-anonymized and linked to real identities through exchange cooperation.
Ares market accepted Bitcoin as secondary cryptocurrency despite tracing risks. Users who sent Bitcoin to The platform during exit scam period lost funds AND created permanent blockchain evidence of darknet marketplace usage. Monero provides superior privacy but cannot prevent administrator theft in centralized marketplaces.
For additional Bitcoin privacy, users can employ Wasabi Wallet with CoinJoin mixing, though this provides weaker privacy than Monero's protocol-level protections. Research proper OPSEC through Privacy Guides comprehensive resources.
Escrow Systems & Trust Mechanisms in Anonymous Markets
Escrow systems function as trust intermediaries in anonymous marketplaces where buyer-vendor transactions lack traditional legal recourse or identity verification. When functioning correctly, escrow holds buyer funds in intermediate custody until delivery confirmation, protecting buyers from vendor non-delivery while protecting vendors from non-payment. However, centralized escrow administration creates single point of failure enabling exit scams when operators control private keys for all escrowed cryptocurrency.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Escrow
Traditional centralized escrow employed by most darknet marketplaces grants administrators unilateral access to escrow wallets through private key control. Platform generates deposit addresses, holds cryptocurrency in administrator-controlled wallets, and releases funds based on buyer finalization or dispute resolution. This architecture enables exit scams - administrators simply transfer all escrowed funds to personal wallets and disappear, as demonstrated by dozens of marketplace failures including recent Abacus and Nexus exit scams.
Multisignature (multisig) escrow provides cryptographic protection against administrator theft through distributed key control. Proper 2-of-3 multisig implementation requires three private keys (buyer, vendor, marketplace) with any two signatures needed for fund release. Normal transaction flow has buyer and vendor signing together, while disputes require marketplace arbitration signing with either party. Crucially, marketplace alone cannot steal funds - attempted unilateral access fails without buyer or vendor cooperation.
True multisig implementation remains extremely rare despite frequent marketing claims. Blockchain verification shows 95%+ of platforms claiming multisig actually use centralized escrow with administrative key control. Projects like OpenBazaar attempted fully decentralized peer-to-peer transactions eliminating escrow entirely, but suffered from poor user experience and vendor discovery challenges. Smart contract escrow on platforms like Ethereum enables trustless cryptocurrency locking with predetermined release conditions, but creates permanent blockchain records reducing transaction privacy compared to Monero-based systems.
Trust Rating Systems & Vulnerabilities
Marketplace trust systems aggregate vendor ratings, transaction counts, and account age to signal reliability. However, trust ratings provide zero protection against platform-wide exit scams - highly-rated vendors lose funds alongside buyers when administrators steal escrow cryptocurrency. Trust ratings also suffer from manipulation through fake reviews, selective scamming (vendor maintains good ratings until exit scam), and account takeovers where established accounts get compromised and used for fraud.
External trust indicators like operational duration (marketplace age), community reputation on forums like Dread, security audits, and verified multisig implementation provide better platform-level risk assessment. However, even long-standing trusted platforms can exit scam - Abacus operated 4 years building stellar reputation before stealing $100M+ in June 2025, demonstrating trust accumulation itself becomes exit scam strategy maximizing theft potential.
Password Management & Account Security
Strong password management prevented account compromise on marketplaces like Ares market. Even after exit scam, proper password security remains essential for cryptocurrency wallets, email accounts, and any remaining marketplace accounts users may maintain elsewhere.
Password Security Best Practices
Use password managers like KeePassXC (open-source, offline) to generate unique 20+ character passwords for every account. The platform users who reused passwords across multiple markets faced account compromise when databases leaked or were seized by law enforcement during exit scams.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) using PGP keys rather than phone-based authentication that creates real identity links. Official Ares market implemented PGP-based 2FA where users signed login challenges with private keys. Store password database in encrypted container using VeraCrypt, never sync to cloud services that could leak credentials.
Account Recovery Risks
Marketplace account recovery features are attack vectors for exit scams and law enforcement. Ares market reportedly ignored account recovery requests during exit scam period, with support tickets deleted without response. Users who lost The platform access had zero recourse for fund recovery due to anonymous administrators and irreversible cryptocurrency transactions.
For ongoing security, use unique email addresses per marketplace (created through Tor), avoid personal information in usernames or profiles, and maintain separate PGP identities for different platforms. When marketplace exit scams occur like Ares market, immediately change all passwords and generate new PGP keys to prevent cross-platform compromise.
Link Verification & Phishing Prevention
Phishing attacks targeting marketplace users are epidemic in darknet ecosystem. Fake Ares market websites continue operating post-exit scam, attempting to steal cryptocurrency and credentials from uninformed users. Link verification and phishing detection are critical security skills for anyone researching darknet marketplaces.
Onion Link Verification Methods
Verify marketplace onion addresses through multiple independent sources: Dread forum, Dark.fail directory, trusted marketplace comparison sites, and PGP-signed announcements. The platform published official onion addresses signed with PGP key, allowing cryptographic verification that links originated from actual administrators rather than phishers.
Check for v3 onion addresses (56 characters, improved security) rather than deprecated v2 format (16 characters). Bookmark verified addresses in Tor Browser, never trust clearnet sites claiming to list "official Ares links," and verify URL exactly character-by-character before entering credentials or sending cryptocurrency.
Phishing Red Flags
Phishing indicators include login pages demanding PIN before PGP verification, withdrawal requiring additional "security deposits," support requesting private keys or seed phrases, unsigned messages claiming to be from official The platform administrators, and URLs with minor character variations (ares vs ar3s, .onion vs .oni0n).
During Ares market exit scam period, phishing sites multiplied to exploit confused users searching for official marketplace. These fake Ares websites steal cryptocurrency sent for orders and collect credentials for identity theft. Any remaining operational "Ares market" sites should be assumed phishing given confirmed exit scam status.
Use OnionShare for secure file sharing, verify PGP signatures on all marketplace communications through OpenPGP standard implementations, and research security practices through Electronic Frontier Foundation resources.
OPSEC Principles for Anonymous Operations
Operational Security (OPSEC) prevents information leakage that could compromise anonymity. Ares market users who practiced poor OPSEC faced risks from law enforcement tracking, marketplace administrator logging, vendor cooperation with authorities, and database seizures during exit scam or law enforcement raids.
Critical OPSEC Requirements
Use Tails OS amnesic operating system or Whonix isolation platform for marketplace access. Never use personal devices, home networks, or regular operating systems when accessing The platform or researching darknet markets. These specialized operating systems provide amnesia (no persistent storage), Tor isolation, and protection against malware persistence.
Advanced users should consider Qubes OS for compartmentalization, running Whonix in isolated virtual machines. Never mix clearnet and darknet activities, use unique pseudonyms per marketplace, avoid discussing marketplace activity on clearnet social media, and minimize metadata creation through careful browsing habits.
Law Enforcement Risks
Marketplace seizures expose complete user databases including order history, cryptocurrency addresses, PGP-encrypted messages, and server logs. Ares market exit scam likely means administrators retain all data for potential future law enforcement cooperation deals. Users should assume their The platform activity is permanently recorded.
Controlled deliveries (law enforcement allowing package delivery then arresting recipient) remain primary arrest vector. Refuse packages if delivery requires signature, never admit ownership of delivered packages, maintain plausible deniability for deliveries, and consult legal representation immediately if law enforcement contact occurs.
Legal Risks & Law Enforcement Investigation Tactics
Darknet marketplace participation carries severe legal risks regardless of platform security measures or anonymity tools employed. Law enforcement agencies worldwide dedicate specialized cybercrime units to darknet investigation including FBI Cyber Division, Europol Joint Cybercrime Action Taskforce (J-CODE), DEA Cyber Crimes Unit, and national agencies across dozens of countries. International cooperation enables cross-border prosecutions as demonstrated by Archetyp marketplace seizure in June 2024 with administrator arrested in Barcelona through coordinated Europol operation.
Investigation Methodologies
Law enforcement employs multiple parallel investigation approaches targeting different vulnerability layers. Network-level attacks include Tor exit node monitoring, traffic correlation analysis, and timing attacks attempting to de-anonymize users despite Tor encryption. These techniques require significant resources and generally target high-value vendors or administrators rather than individual buyers.
Physical interdiction provides more reliable evidence through controlled deliveries where law enforcement intercepts packages, documents contents, and delivers under surveillance monitoring for pickup confirmation. Successful controlled delivery creates nexus between package contents and physical identity, enabling search warrants for devices, financial records, and additional evidence. Package interception combined with cooperative vendor testimony (vendors offered reduced sentences for buyer cooperation) enables prosecution even when online identity remains technically anonymous.
Database seizures during marketplace takedowns expose complete user activity including order history, cryptocurrency addresses, encrypted messages (metadata visible even when content encrypted), vendor communications, and server logs. Exit scams potentially create law enforcement cooperation opportunities where fleeing administrators trade user databases for leniency or immunity. Users should assume all marketplace activity creates permanent forensic evidence potentially accessible to law enforcement through multiple vectors regardless of anonymity tool sophistication.
Cryptocurrency Tracing
Blockchain analysis firms including Chainalysis, CipherTrace, and Elliptic specialize in tracing cryptocurrency transactions through clustering algorithms, exchange cooperation, and heuristic analysis. Bitcoin's transparent blockchain enables linking marketplace transactions to exchange accounts with full KYC (Know Your Customer) identity verification including passport scans, address verification, and banking information.
Even privacy-focused practices like CoinJoin mixing and intermediate wallet hopping leave traceable patterns analyzable through machine learning algorithms. Law enforcement can request exchange records years after transactions, creating long-term prosecution risk. Cryptocurrency seizure authority enables government confiscation of all funds traced to illegal activity including marketplace transactions, even from users who never received purchased items due to vendor scams or platform exit scams.
Platform Navigation
Explore our comprehensive Ares market information and security guides:
- Complete Ares Guide - Tor setup, PGP encryption, cryptocurrency wallets, and OPSEC practices for marketplace security research
- Security Analysis - Advanced OPSEC, exit scam indicators, law enforcement risks, and security architecture analysis
- Frequently Asked Questions - Common questions about The platform exit scam, marketplace security, and cryptocurrency privacy
- About Ares Market - Detailed platform information, market history, technical features, and exit scam timeline
- Access Information - Educational information about marketplace link verification and phishing prevention (NO ACTIVE LINKS - exit scam occurred)
Authoritative External Resources
Essential privacy, security, and cryptocurrency resources from trusted organizations: